Are you thinking about starting your business in Malaysia? With a population of over 34 million and a strong economy, Malaysia offers plenty of opportunities for entrepreneurs. It ranks 12th globally for ease of business, making it an attractive destination. Setting up a business in Malaysia can be rewarding, given its strategic location, diverse economy, and business-friendly environment.
Navigating the business setup process in Malaysia can be complex, especially with the various legal and regulatory requirements.
In this blog we will help you understand the steps to get your business up and running in Malaysia. We cover everything you need to know, from selecting the appropriate business structure and registering your company to securing the necessary licenses and understanding tax obligations.
Steps to Start a Business in Malaysia
1. Choose Your Business Idea and Plan
First, figure out what kind of business you want to start. Think about:
- Who is your target market? Who will buy your product or service?
- What problem are you solving? What makes your business valuable?
- Do a SWOT analysis: Identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Make a business plan: Outline how much money you need, where your funding will come from, and how you’ll market your business.
2. Choose a Business Name
Your business name should be unique, easy to remember, and related to what you do. Before finalising, check if the domain name is available for a website and do an official name search through Suruhanjaya Syarikat Malaysia (SSM) to ensure it’s not taken. You can check your name through our free Malaysia Company name check tool.
3. Find a Business Location
If your business needs a physical store or office, choose a location that suits your needs. However, you can skip this step if you run an online or home-based business.
4.Preparing for Business Registration
The first and foremost step in registering a company is deciding on the basic requirements, which include choosing a business structure that works for your firm, naming the company, selecting and appointing qualified officials, and finalising registration and capital needs.
-
Choose a Business Structure
The first step in establishing or incorporating a company in Malaysia is to choose a suitable business entity. You should research each entity to decide which best matches your goals and objectives. Decide whether you want a sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability partnership, private limited company (Sdn Bhd), public limited company (Bhd), or a branch of a foreign company.
Read our guide on 5 Types of Business Entities in Malaysia to learn how to choose the correct entity.
-
Register Your Business Name
Once you have chosen a suitable business entity, the next thing to do is select a company name. After you have decided on a name, you should run a name check with the Companies Commission of Malaysia (SSM). When the name check is completed, you can register the name with the SSM. Upon approval, the name will be reserved for your company.
-
Appoint Key Managerial Personnel
Every company needs to follow minimum criteria listed below while setting up a company in malaysia:
- One director (18 years or older, a natural person, not a company)
- One shareholder (can be a person or a corporate entity)
- A company secretary (must be licensed by SSM)
-
Provide a Registered Office Address
When starting a company in Malaysia, a registered office address is mandatory for official communication with the Companies Commission of Malaysia (SSM) and other authorities, and it must be a legitimate commercial address, (P.O. boxes are prohibited). All statutory records, registers, minute books, and the common seal are required to be kept in the registered office.
-
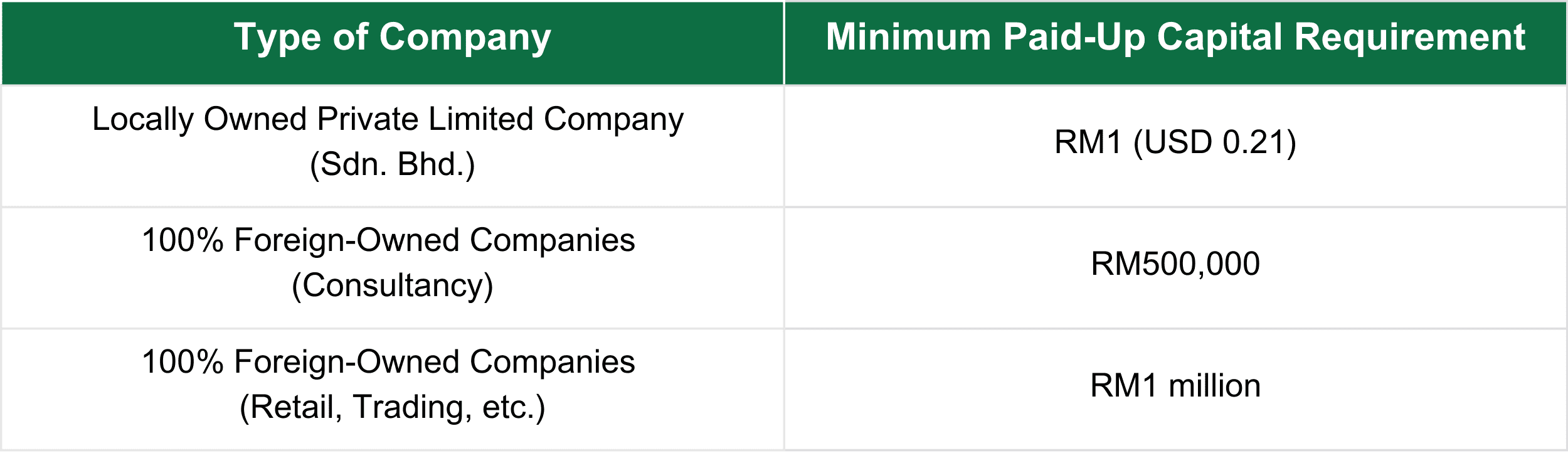
Decide on Share Capital
The minimum required share capital for incorporating a company in Malaysia depends on your business type.
5. Registering Your Company in Malaysia
Once your name is approved, you must register your company with SSM. You can do this online via the MyCold portal or visit an SSM counter. The standard registration fee is RM 1,010. Documents required are:
- Memorandum and Article of Association / Constitution
- Statutory Declaration by A Director or Promoter Before Appointment
- Declaration of Compliance (Form 201)
- Company name’s approval letter from SSM (one copy).
- Identity card of every director and company secretary (Form 48A & 49).
Details regarding documents are discussed in detail in this blog.
Receive Your Business Incorporation Certificate
If everything checks out, SSM will issue your Certificate of Incorporation within 1–3 days.
6. Post Registration
-
Open a Corporate Bank Account
You’ll need to open a corporate bank account in Malaysia to manage your business finances effectively. Most banks require the following documents to open a business bank account:
- Certificate of Incorporation
- Board Resolution
- Identification documents of directors and signatories
- Business registration documents
- Relevant licenses or permits (if applicable)
-
Get Business Licenses and Permits
Additional licenses or permits can be required, depending on the nature of your firm. These are a few common examples of licenses and permits in malaysia
- Business Premise License (for offices and retail stores)
- Halal Certification (for enterprises that deal with food)
- Obtaining a license for import/export (if you’re involved in foreign trade)
Check with the Malaysia Business Licensing System (MBLS) or your local municipal council for detailed requirements.
-
Understand Your Tax Obligations
According to Malaysian regulations, all companies must register for corporate income tax within three months of starting operations. To do so, they must apply to the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (LHDN) and obtain their tax ID. Refer FAQ 2 for more on Tax structure in Malaysia.
-
Appoint an Auditor
Every company must appoint an auditor before the first annual general meeting. Annual general meetings are not mandatory for private limited companies. In the case of newly incorporated companies, the board of directors shall appoint the first auditor at least 30 days before the end of the period for submitting the first financial statements.
-
Register for the Employee Provident Fund (EPF)
Both employers and employees need to contribute. As an employer, you must make mandatory employee contributions to the Employees Provident Fund (EPF), Social Security Organisation (SOCSO), and Employment Insurance System (EIS).
-
Submit Annual Returns & Keep Financial Records
Submit your Annual Return to SSM within 30 days of your incorporation anniversary to keep company details, including directors and shareholders, up to date. Maintain proper financial records and ensure financial statements are audited unless your company qualifies for an exemption.
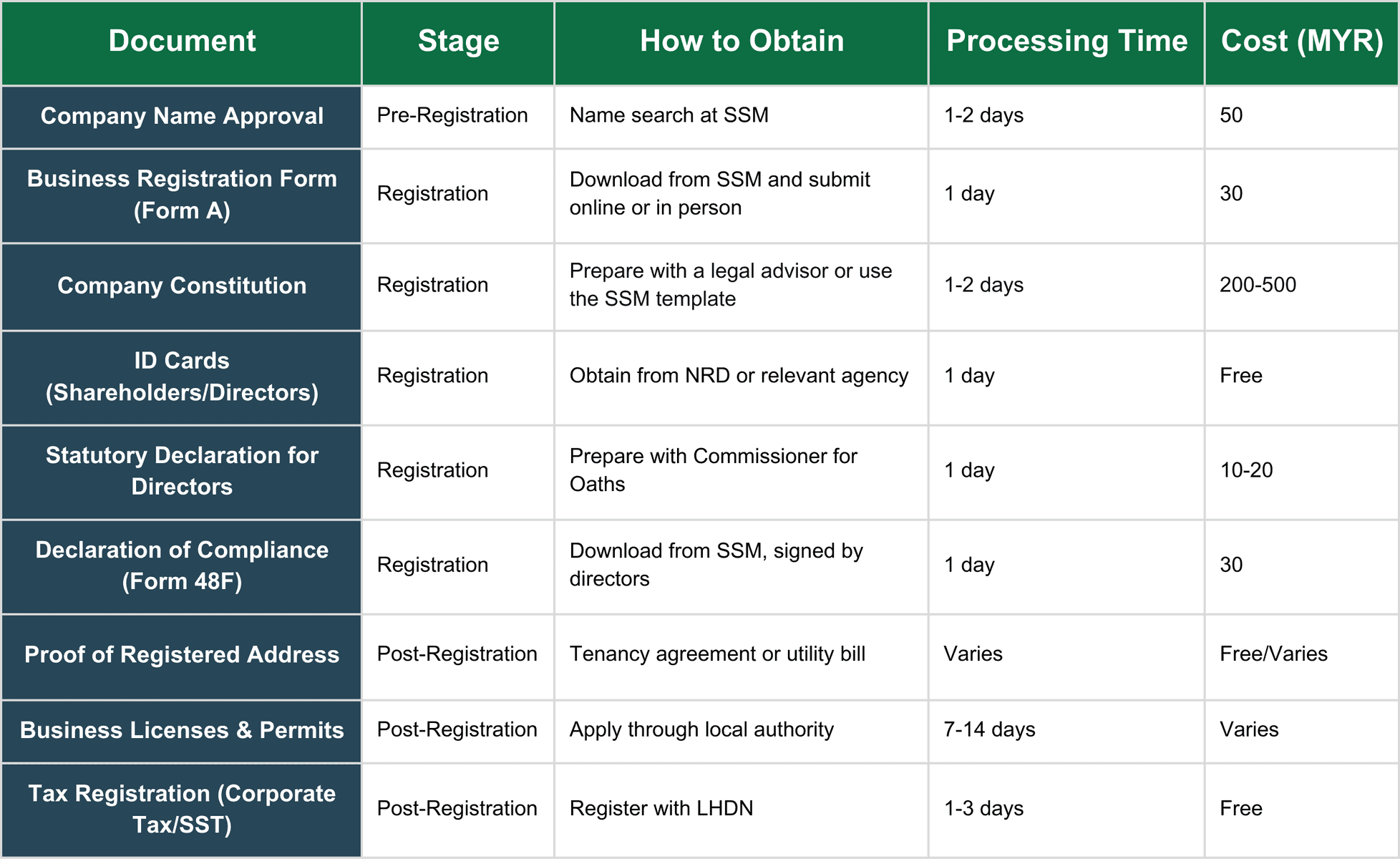
Here is an overview of the necessary documents for starting a business in Malaysia.
Best Industries for setting up businesses in Malaysia
Malaysia has a diverse and growing economy. Here are some of the best industries for new businesses who aspire to set up their business in Malaysia:
- Manufacturing: Electronics, machinery, and consumer goods. The government offers tax incentives for high-tech industries.
- Information Technology (IT): The Multimedia Super Corridor (MSC) provides tax holidays and other benefits for tech companies.
- Tourism and Hospitality: A vast industry, from hotels and resorts to travel agencies and transportation services.
- Green Technology and Renewable Energy: Malaysia invests heavily in solar energy, sustainable agriculture, and environmental services.
- Education and Healthcare: There’s a rising demand for private schools, colleges, hospitals, and specialised healthcare services.
Key government agencies and organisations offering support to business in Malaysia
Several government agencies provide support for businesses in Malaysia. Here are the key ones:
- Ministry of Entrepreneur Development and Cooperatives (MEDAC): Provides training, financial aid, and advisory services.
- Small and Medium Enterprises Corporation Malaysia (SME Corp.): Develops policies and programs for SMEs.
- Malaysia External Trade Development Corporation (MATRADE): Promotes exports and helps businesses expand internationally.
- Pertubuhan Keselamatan Sosial (PERKESO): Social security for employees in work-related accidents or diseases.
- Suruhanjaya Syarikat Malaysia (SSM): Regulates business registration and compliance.
- The Companies Commission of Malaysia (CCM): Handles business registration and renewals.
- Human Resources Development Fund (HRDF): Helps develop local talent and workforce.
- Malaysian Investment Development Authority (MIDA): Advises on investment opportunities and incentives.
Conclusion
Starting a business in Malaysia can be a rewarding experience, but the setup process can be complex. Following this guide gives you a clear roadmap for running your business smoothly. Each step is crucial for your success, from choosing your business idea and structure to registering your company and understanding tax obligations.
If you want to register a company in Malaysia, 3E Accounting Services can help you with the entire process, ensuring a smooth and hassle-free experience.
At 3E Accounting, we understand the complexities of business registration, compliance, and taxation in Malaysia. With our cost-effective, efficient, and results-driven approach, we provide expert guidance to help you make informed decisions and ensure seamless business incorporation.
Start Your Malaysia Business Journey Today
Set up your business in Malaysia with ease! 3E Accounting Services guides you through every step for a seamless setup.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Company Act 2016 is the primary legislation governing business incorporation in Malaysia.The process is streamlined and efficient, with clear guidelines to follow. However, foreign entrepreneurs need to be aware of some details before starting the incorporation process.
The tax structure that applies to all residents and non-residents incorporating their business in Malaysia are:
a) Personal income tax for non-residents of 30% on their taxable earnings.
b) Corporate income tax is charged at a rate of 24% (for residents and non-residents setting up a company in Malaysia).
c) Service tax is charged at a rate of 8% on all the taxable services.
d) Stamp duty tax on the legal papers.
Yes, a foreign entrepreneur is free to register a company in Malaysia only after fulfilling certain legal requirements for setting up a company in Malaysia such as having at least 1 director who is a resident of Malaysia. A private limited company commonly known as Sendirian Berhad (Sdn Bhd) is a common choice for foreign investors. Foreigners can own 100% of the company.
Common challenges include understanding local regulations, hiring local talent, and navigating industry-specific regulatory bodies.
To start a small business in Malaysia, research your idea, choose a business structure (like sole proprietorship or a company), register your business with SSM, obtain necessary licenses and permits, open a bank account, and register for tax.
Based on the various factors, the estimated initial cost to start a small to medium-sized business in Malaysia might range from RM 50,000 to RM 150,000.
Abigail Yu
Author
Abigail Yu oversees executive leadership at 3E Accounting Group, leading operations, IT solutions, public relations, and digital marketing to drive business success. She holds an honors degree in Communication and New Media from the National University of Singapore and is highly skilled in crisis management, financial communication, and corporate communications.